1. 들어가며
JPA로 작업하다 보면 N+1 문제에 맞닥뜨리게 되는데요. N+1은 언제 발생할 수 있는 이슈이고 이를 해결하기 위해서 어떤 방법들이 있는지 알아보자.
2. 개발 환경
포스팅에서 언급한 코드는 github에 올라가 있다.
- OS : Mac OS
- IDE: Intellij
- Java : JDK 1.8
- Source code : github
- Software management tool : Maven
3. N+1 문제 및 해결 방법
JPA에서 N+1 발생 시 성능에 큰 영향을 줄 수 있기 때문에 JPA로 개발하고 있다면 꼭 알아두어야 하자. N+1은 언제 발생할 수 있는 같이 알아보자.
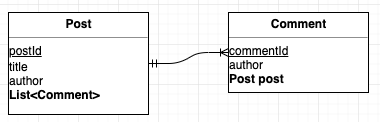
Post와 Comment 엔티티는 다음과 같다.
3.1 N+1 문제 발생 케이스
3.1.1 즉시 로딩 (fetchType.EAGER) 변경후 findAll()로 조회하는 경우
Post와 Comment 엔티티 간에 다대일 양방향 연관 관계이다. @OneToMany 언노테이션의 fetch의 기본값은 지연 로딩이지만, 즉시 로딩으로 변경하면 N+1 문제가 발생할 수 있다.
@Table(name = "post")
public class Post extends DateAudit {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "post_id")
private Long postId;
@JsonIgnore //JSON 변환시 무한 루프 방지용
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "post", fetch = FetchType.EAGER) //즉시로딩으로 변경한 경우
private List<Comment> commentList = new ArrayList<>();
}
@Table(name = "comment")
public class Comment extends DateAudit {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "comment_id")
private Long commentId;
//연관관계 매팽
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
@JoinColumn(name = "post_id", nullable = false)
private Post post;
}
findAll() 메서드로 Post 전체를 조회해보자.
@Test
public void test_N1_문제_발생_즉시로딩_하는_경우() throws JsonProcessingException {
savePostWithComments(4, 2);
List<Post> posts = postRepository.findAll(); //N+1 발생한다
}
4개의 Post와 각 Post에 2개의 Comment를 생성하고 나서 findAll() 메서드로 조회한다.
실제 실행되는 쿼리를 살펴보면 먼저 Post select 쿼리를 실행한다. 그리고 해당 Post에 대해서 Comment를 조회하기 위해서 Post의 수만큼 4번의 쿼리가 추가로 발생한다. 데이터의 수만큼 조회하는 것을 N+1 문제라고 한다. 데이터가 많을수록 쿼리 해야 하는 수가 많아져서 성능에도 큰 영향을 주게 된다.
Hibernate: select post0_.post_id as post_id1_1_, post0_.create_dt as create_d2_1_, post0_.updated_dt as updated_3_1_, post0_.author as author4_1_, post0_.content as content5_1_, post0_.like_count as like_cou6_1_, post0_.title as title7_1_ from post post0_
Hibernate: select commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_1_, commentlis0_.create_dt as create_d2_0_1_, commentlis0_.updated_dt as updated_3_0_1_, commentlis0_.author as author4_0_1_, commentlis0_.content as content5_0_1_, commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_1_ from comment commentlis0_ where commentlis0_.post_id=?
Hibernate: select commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_1_, commentlis0_.create_dt as create_d2_0_1_, commentlis0_.updated_dt as updated_3_0_1_, commentlis0_.author as author4_0_1_, commentlis0_.content as content5_0_1_, commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_1_ from comment commentlis0_ where commentlis0_.post_id=?
Hibernate: select commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_1_, commentlis0_.create_dt as create_d2_0_1_, commentlis0_.updated_dt as updated_3_0_1_, commentlis0_.author as author4_0_1_, commentlis0_.content as content5_0_1_, commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_1_ from comment commentlis0_ where commentlis0_.post_id=?
Hibernate: select commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_1_, commentlis0_.create_dt as create_d2_0_1_, commentlis0_.updated_dt as updated_3_0_1_, commentlis0_.author as author4_0_1_, commentlis0_.content as content5_0_1_, commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_1_ from comment commentlis0_ where commentlis0_.post_id=?
가장 빠르게 해결하는 방법은 지연 로딩으로 변경하는 것이다.
@Table(name = "post")
public class Post extends DateAudit {
...(생략)...
@JsonIgnore //JSON 변환시 무한 루프 방지용
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "post", fetch = FetchType.LAZY) //LAZY로 변경
private List<Comment> commentList = new ArrayList<>();
}
@Transactional
@Test
public void test_N1_문제_발생_지연로딩_하는_경우() throws JsonProcessingException {
savePostWithComments(4, 2);
List<Post> posts = postRepository.findAll(); //N+1 발생하지 않음
}
변경 이후 findAll() 메서드로 호출하면 지연 로딩이기 때문에 Post select 쿼리만 실행된다.
Hibernate: select post0_.post_id as post_id1_1_, post0_.create_dt as create_d2_1_, post0_.updated_dt as updated_3_1_, post0_.author as author4_1_, post0_.content as content5_1_, post0_.like_count as like_cou6_1_, post0_.title as title7_1_ from post post0_
지연 로딩은 실제 Comment의 값을 조회하는 경우에만 해당 select 쿼리가 발생한다.
log.info("post : {}", posts.get(0).getCommentList()); //조회 쿼리가 실행된다
Hibernate: select commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_1_, commentlis0_.create_dt as create_d2_0_1_, commentlis0_.updated_dt as updated_3_0_1_, commentlis0_.author as author4_0_1_, commentlis0_.content as content5_0_1_, commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_1_ from comment commentlis0_ where commentlis0_.post_id=?
이미 짐작하셨겠지만, loop으로 조회하면 즉시 로딩하는 것과 같은 결과가 발생한다.
3.1.2 지연 로딩(LAZY) 변경 + Loop으로 조회하는 경우
@OneToMany에서 fetch를 지연 로딩으로 변경한 이후에 loop으로 조회해보자.
@Table(name = "post")
public class Post extends DateAudit {
...(생략)...
@JsonIgnore //JSON 변환시 무한 루프 방지용
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "post", fetch = FetchType.LAZY) //LAZY로 변경후
private List<Comment> commentList = new ArrayList<>();
}
@Transactional
@Test
public void test_N1_문제_발생_지연로딩설정_loop으로_조회하는_경우() throws JsonProcessingException {
savePostWithComments(4, 2);
List<Post> posts = postRepository.findAll(); //N+1 발생하지 않는다
List<Comment> commentList;
for (Post post : posts) {
commentList = post.getCommentList();
log.info("post author: {}", commentList.size()); //N+1 발생한다
}
}
3.1.1에서와 같이 동일하게 N+1 이슈가 발생한다.
Hibernate: select post0_.post_id as post_id1_1_, post0_.create_dt as create_d2_1_, post0_.updated_dt as updated_3_1_, post0_.author as author4_1_, post0_.content as content5_1_, post0_.like_count as like_cou6_1_, post0_.title as title7_1_ from post post0_
Hibernate: select commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_1_, commentlis0_.create_dt as create_d2_0_1_, commentlis0_.updated_dt as updated_3_0_1_, commentlis0_.author as author4_0_1_, commentlis0_.content as content5_0_1_, commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_1_ from comment commentlis0_ where commentlis0_.post_id=?
Hibernate: select commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_1_, commentlis0_.create_dt as create_d2_0_1_, commentlis0_.updated_dt as updated_3_0_1_, commentlis0_.author as author4_0_1_, commentlis0_.content as content5_0_1_, commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_1_ from comment commentlis0_ where commentlis0_.post_id=?
Hibernate: select commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_1_, commentlis0_.create_dt as create_d2_0_1_, commentlis0_.updated_dt as updated_3_0_1_, commentlis0_.author as author4_0_1_, commentlis0_.content as content5_0_1_, commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_1_ from comment commentlis0_ where commentlis0_.post_id=?
Hibernate: select commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_1_, commentlis0_.create_dt as create_d2_0_1_, commentlis0_.updated_dt as updated_3_0_1_, commentlis0_.author as author4_0_1_, commentlis0_.content as content5_0_1_, commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_1_ from comment commentlis0_ where commentlis0_.post_id=?
3.1.3 N+1이 발생하는 원인
JpaRepository에 정의한 인터페이스 메서드를 실행하면 JPA는 메서드 이름을 분석해서 JPQL를 생성하여 실행하게 된다. JPQL은 SQL을 추상화한 객체지향 쿼리 언어로서 특정 SQL에 종속되지 않고 엔티티 객체와 필드 이름을 가지고 쿼리를 한다.
그면 지연 로딩 + loop으로 조회 시 왜 N+1 쿼리가 생성이 되어 실행되는지 알아보자.
@Transactional
@Test
public void test_N1_문제_발생_지연로딩설정_loop으로_조회하는_경우() throws JsonProcessingException {
savePostWithComments(4, 2);
List<Post> posts = postRepository.findAll(); //(1) N+1 발생하지 않는다
List<Comment> commentList;
for (Post post : posts) {
commentList = post.getCommentList();
log.info("post author: {}", commentList.size()); //(2) N+1 발생한다
}
}
(1) 지연로딩으로 findAll() 실행시 Post 객체 관련된 정보를 조회한다.
select post0_.post_id as post_id1_1_, post0_.create_dt as create_d2_1_, post0_.updated_dt as updated_3_1_, post0_.author as author4_1_, post0_.content as content5_1_, post0_.like_count as like_cou6_1_, post0_.title as title7_1_ from post post0_
(2) 여기서 Comment 정보를 조회하면, Post에 대한 조회는 이미 끝난 상태라서 JOIN으로 쿼리가 생성이 안 된다. 단지 Post에 대한 정보 ID로 조회할 수밖에 없어서 where comment.postId=? 형식으로 JPQL 쿼리를 생성한다. 이로 인해 매번 조회 쿼리가 생성이 되어 N 번 실행하는 이슈가 발생한다.
Hibernate: select commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_0_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_1_, commentlis0_.create_dt as create_d2_0_1_, commentlis0_.updated_dt as updated_3_0_1_, commentlis0_.author as author4_0_1_, commentlis0_.content as content5_0_1_, commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_1_ from comment commentlis0_ where commentlis0_.post_id=?
3.2 해결 방안
N+1을 어떻게 해결할 수 있는지에 대해서 알아보자.
3.2.1 JPQL 페치 조인 사용 - 추천
JPQL에 fetch join 키워드를 사용해서 join 대상을 함께 조회할 수 있다. Post 조회 시 p.commentList도 같이 join 해서 조회해옵니다.
@Repository
public interface PostRepository extends JpaRepository<Post, Long> {
@Query("select p from Post p left join fetch p.commentList")
List<Post> findAllWithFetchJoin();
}
지연 로딩 설정 이후에 loop을 사용하면 그전 예제에서는 N+1이 발생했지만, findAllWithFetchJoin() 메서드 실행때에는 관련 대상을 한 번에 조회하여 N+1 이슈가 발생하지 않는다.
@Transactional
@Test
public void test_N1_문제_해결방법_fetch_join_사용() {
savePostWithComments(4, 2);
List<Post> posts = postRepository.findAllWithFetchJoin(); //한번에 조회해온다.
List<Comment> commentList;
for (Post post : posts) {
commentList = post.getCommentList();
log.info("post author: {}", commentList.size()); //N+1 발생하지 않는다
}
}
로그에서도 left outer join으로 조회해 오는 것을 볼 수 있다.
Hibernate: select post0_.post_id as post_id1_1_0_, commentlis1_.comment_id as comment_1_0_1_, post0_.create_dt as create_d2_1_0_, post0_.updated_dt as updated_3_1_0_, post0_.author as author4_1_0_, post0_.content as content5_1_0_, post0_.like_count as like_cou6_1_0_, post0_.title as title7_1_0_, commentlis1_.create_dt as create_d2_0_1_, commentlis1_.updated_dt as updated_3_0_1_, commentlis1_.author as author4_0_1_, commentlis1_.content as content5_0_1_, commentlis1_.post_id as post_id6_0_1_, commentlis1_.post_id as post_id6_0_0__, commentlis1_.comment_id as comment_1_0_0__ from post post0_ left outer join comment commentlis1_ on post0_.post_id=commentlis1_.post_id
3.2.2 Batch Size 지정 + 즉시 로딩
JPQL 페치 조인 대신 Batch 크기를 지정하는 방법도 있다. @BatchSize 어노테이션에 size를 지정하고 fetch 타입은 즉시로 설정한다.
@Table(name = "post")
public class Post extends DateAudit {
...(생략)...
@JsonIgnore //JSON 변환시 무한 루프 방지용
@BatchSize(size = 2) //batch size를 지정한다
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "post", fetch = FetchType.EAGER) //즉시로딩으로 변경한다
private List<Comment> commentList = Lists.newArrayList();
}
@Transactional
@Test
public void test_N1_문제_해결방법_증시로딩설정_loop으로_조회하는_경우() throws JsonProcessingException {
savePostWithComments(4, 2);
List<Post> posts = postRepository.findAll(); //배치 사이즈만큼 조회해온다
}
Hibernate: select post0_.post_id as post_id1_1_, post0_.create_dt as create_d2_1_, post0_.updated_dt as updated_3_1_, post0_.author as author4_1_, post0_.content as content5_1_, post0_.like_count as like_cou6_1_, post0_.title as title7_1_ from post post0_
Hibernate: select commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_1_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_1_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_0_, commentlis0_.create_dt as create_d2_0_0_, commentlis0_.updated_dt as updated_3_0_0_, commentlis0_.author as author4_0_0_, commentlis0_.content as content5_0_0_, commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_0_ from comment commentlis0_ where commentlis0_.post_id in (?, ?)
Hibernate: select commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_1_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_1_, commentlis0_.comment_id as comment_1_0_0_, commentlis0_.create_dt as create_d2_0_0_, commentlis0_.updated_dt as updated_3_0_0_, commentlis0_.author as author4_0_0_, commentlis0_.content as content5_0_0_, commentlis0_.post_id as post_id6_0_0_ from comment commentlis0_ where commentlis0_.post_id in (?, ?)
findAll()로 호출할 때마다 where in 쿼리를 이용해서 배치 사이즈만큼 조회해옵니다. 배치 사이즈를 넘는 경우에는 추가로 조회해오는 쿼리가 생성된다.
Batch 사이즈 지정으로 해결하는 방법은 글로벌 패치 전략을 즉시 로딩으로 변경해야 하고 또한 배치 사이즈만큼만 조회할 수 있어서 N+1 문제를 완벽하게 해결하지 않아 권장하는 해결방법은 아닙니다.
4. FAQ
4.1 JPA의 글로벌 페치 전략 기본 값은 어떻게 되나요?
- 즉시 로딩 (EAGER)
- @OneToOne
- @ManyToOne
- 지연 로딩 (LAZY)
- @OneToMany
- @ManyToMany
4.2 페치 조인 사용시 주의사항은 없나?
페치 조인은 연관된 엔티티를 한번에 조회할 수 있어서 조회 횟수를 줄여 성능 최적화시 많이 사용된다. 하지만, 페치 조인은 다음과 같은 한계점이 존재한다.
참고 - 책 : 자바 ORM 표준 JPA 프로그래밍
- 페체 조인에 alias 별칭을 사용할 수 없다
- 둘 이상의 컬렉션을 페치할 수 없다
- 콜렉션 구현체에 따라서 페치도 가능하지만, 안되는 경우도 있어서 주의가 필요하다
- 컬렉션을 페치 조인하면 paging API를 사용할 수 없다
- 컬렉션을 페치 조인하고 페이징 API를 사용하면 경고 로그를 남기면서 메모리에서 페이징 처리를 한다.
- 데이터가 많아지면, 메모리 초과 예외가 발생할 수 있다
- 컬렉션(일대다)는 페이징 API를 사용할 수 없다
- 단일 값 연관 필드(일대일, 다대일)에서는 페치 조인을 사용할 수 있다.
- 컬렉션을 페치 조인하고 페이징 API를 사용하면 경고 로그를 남기면서 메모리에서 페이징 처리를 한다.
5. 참고
- JPA N+1
- 책 : 자바 ORM 표준 JPA 프로그래맹